Available courses
Faculty members of IIT Goa may:
1. discuss various instructional and assessment strategies
2. comment on the pros and cons of various online teaching related software and hardware
3. Upload documents of relevance under a topic created by them in a section (total 14 sections) in the course site
- Teacher: Anirudha Ambekar
- Teacher: Sreejith AV
- Teacher: Dhirendra Bahadur
- Teacher: Saumya Bajpai
- Teacher: Sreenath Balakrishnan
- Teacher: Ashish Bhateja
- Teacher: SOMENATH BISWAS
- Teacher: Arindam Das
- Teacher: Santosh Das
- Teacher: KUNTAL DEKA
- Teacher: Sudakshina Dutta
- Teacher: Sheron Figarado
- Teacher: PRABHU GAUNKAR
- Teacher: Clint George
- Teacher: Sandip Haldar
- Teacher: Sabiha Hashami
- Teacher: Shiva Iyer
- Teacher: Sudipta Kanungo
- Teacher: Neha Karanjkar
- Teacher: Sachin Kore
- Teacher: Arpita Korwar
- Teacher: Santosh Kumar
- Teacher: Shobha Madan
- Teacher: Amaldev Manuel
- Teacher: Barada Kant Mishra
- Teacher: Raja Mitra
- Teacher: Ravi Mittal
- Teacher: Nandakumar N P
- Teacher: Rishikesh Narayan
- Teacher: Sunil Paul
- Teacher: Rajesh Prabhugaonkar
- Teacher: Bidhan Pramanik
- Teacher: Shiv Prasad
- Teacher: Neelakandan R
- Teacher: Rudra ROY
- Teacher: Sujit Sahoo
- Teacher: Sashidhar Sampathirao
- Teacher: Mantu Santra
- Teacher: harpreet Singh
- Teacher: Sharad Sinha
- Teacher: Milind Sohoni
- Teacher: Bidyadhar Subudhi
- Teacher: Thaseem Thajudeen
- Teacher: Lokpati Tripathi
- Teacher: Ponnulakshmi VK
- Teacher: Vaibhav Wasnik
- Teacher: Yogaraj Yograj
Just for Test
- Teacher: Amol Kamble
Course details: https://nehakaranjkar.github.io/cs101.html
- Teacher: Tushar Lone
- Teacher: Neha Karanjkar
- Teacher: Tushar Lone
- Teacher: Raushan Kumar
- Teacher: Divya Mishra
- Teacher: Anshu Moon
- Teacher: CHITRA N
- Teacher: Soumya Pattanayak
- Teacher: Shruti Shet
- Teacher: CHITRA N
- Teacher: Shruti Shet
This is a program elective course for both UG and PG students. Here is a brief syllabus of the course: Review of MOS transistor models, CMOS logic families including static, dynamic and dual rail logic. Integrated circuit layout; design rules, parasites. Building blocks, ALU, Memory and sense amplifier, FIFO, counters, VLSI design: data and control path design, floor planning, Design Technology: introduction to hardware description languages(VHDL), logic, circuit and layout verification. Design examples.
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee636.html
- Teacher: Nandakumar N P
This is a program elective course for both UG and PG students. Here is a brief syllabus of the course: Introduction to CMOS analog integrated circuit design. MOS transistor as the basic design unit: device structure, I-V characteristics, second order effects, SPICE models. Basic amplifier topologies: CS, CG, CD, cascode amplifiers. Differential amplifiers: single ended and differential operation, small signal analysis. Current mirrors: passive and active topologies. Performance parameters of analog circuits: frequency response, noise. Feedback in analog integrated circuits: types of feedback, stability and frequency compensation. Operational amplifiers: topologies, performance parameters. Layout of analog integrated circuits.
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee632.html
- Teacher: Nandakumar N P

This is a core course for EE BTech students. Here is a brief syllabus of the course: Review of basics of digital electronics: Number systems, Boolean algebra, logic gates and circuits, minimization of logic functions. Number representation and arithmetic circuits: Signed and unsigned numbers, binary codes, arithmetic operation of binary numbers-addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Combinational circuit elements: Multiplexers and demultiplexers, decoders and encoders, code converters. Synthesis of combinational logic functions. Cyclic and acyclic logic circuits. Memory elements: latches and flipflops, applications-shift registers, and counters. Sequential circuits and finite state machines: analysis and synthesis. Synchronous and asynchronous sequential circuits. Timing analysis of clocked circuits. Hazards in digital circuits. Transistor level implementation of digital circuit elements: CMOS digital family. Introduction to VHDL and programmable logic devices. Advanced digital system design topics and applications.
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee232.html
- Teacher: Nandakumar N P
- Teacher: Sheron Figarado
- Teacher: SAURABH KUMAR
- Teacher: Diptesh Naik
- Teacher: minerva P
- Teacher: Ishwar Rathod
- Teacher: Ishwar Rathod
- Teacher: Arunima S
- Teacher: Neel Shrivastava
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee660.html
- Teacher: Nandakumar N P
This is a program elective course for both UG and PG students. Here is a brief syllabus of the course: Review of MOSFETs: structure, operation, IV characteristics. CMOS inverter: properties, static and dynamic behavior, power dissipation, optimum sizing. Combinational Circuits: static and dynamic CMOS circuits, complementary CMOS gates, design of CMOS circuit for Boolean expressions, propagation delay, logical effort, path delay optimization, asymmetric and skewed gates, mirror functions, arithmetic circuits. Sequential circuits: types and timing parameters of memory elements, bistable memory elements, design of memory elements. CMOS families: ratioed logic, differential cascode voltage switch logic, pass transistor logic, dynamic logic, etc.
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee635.html
- Teacher: Nandakumar N P
- Teacher: Rohan Burye
- Teacher: Sheron Figarado
- Teacher: Kranthi Panuganthi
This is a program elective course for both UG and PG students. Here is a brief syllabus of the course: Introduction to CMOS analog integrated circuit design. MOS transistor as the basic design unit: device structure, I-V characteristics, second order effects, SPICE models. Basic amplifier topologies: CS, CG, CD, cascode amplifiers. Differential amplifiers: single ended and differential operation, small signal analysis. Current mirrors: passive and active topologies. Performance parameters of analog circuits: frequency response, noise. Feedback in analog integrated circuits: types of feedback, stability and frequency compensation. Operational amplifiers: topologies, performance parameters. Layout of analog integrated circuits.
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee632.html
This is a core course for EE BTech students. Here is a brief syllabus of the course: Review of basics of digital electronics: Number systems, Boolean algebra, logic gates and circuits, minimization of logic functions. Number representation and arithmetic circuits: Signed and unsigned numbers, binary codes, arithmetic operation of binary numbers-addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Combinational circuit elements: Multiplexers and demultiplexers, decoders and encoders, code converters. Synthesis of combinational logic functions. Cyclic and acyclic logic circuits. Memory elements: latches and flipflops, applications-shift registers, and counters. Sequential circuits and finite state machines: analysis and synthesis. Synchronous and asynchronous sequential circuits. Timing analysis of clocked circuits. Hazards in digital circuits. Transistor level implementation of digital circuit elements: CMOS digital family. Introduction to VHDL and programmable logic devices. Advanced digital system design topics and applications.
For further details, visit http://iitgoa.ac.in/~npnandakumar/ee232.html
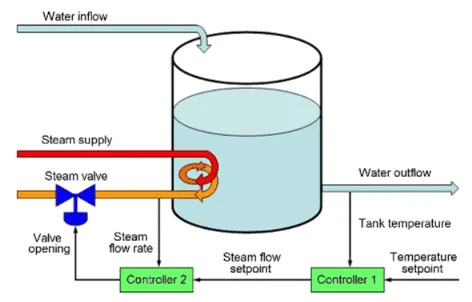
- Teacher: Sai Banoth
- Teacher: Sheron Figarado
- Teacher: Deval Gawas
- Teacher: Nishad N
- Teacher: Neel Shrivastava
- Teacher: Neel Shrivastava
- Teacher: Rudra ROY
- Teacher: Anirudha Ambekar
- Teacher: Arindam Das
- Teacher: Yogaraj Yograj
- Teacher: Arindam Das
- Teacher: Sandipan De
- Teacher: Subash Behera
- Teacher: Debendra kumar Swain
- Teacher: Aditi Tomar
- Teacher: Shobha Madan
- Teacher: Shiv Prasad
- Teacher: Santosh Das
- Teacher: Vaibhav Wasnik
- Teacher: Sudipta Kanungo
- Teacher: Santosh Kumar
- Teacher: Santosh Das
- Teacher: Sudipta Kanungo
- Teacher: Shiva Iyer
- Teacher: Shiva Iyer
- Teacher: Raja Mitra
- Teacher: Rishikesh Narayan
- Teacher: Shiva Iyer
- Teacher: Raja Mitra
- Teacher: Rishikesh Narayan
- Teacher: Shiva Iyer
- Teacher: Raja Mitra
- Teacher: Rishikesh Narayan
- Teacher: Satyaprakash Ahirwar
- Teacher: Program Chair Chemical and Materials Engineering
- Teacher: Program Chair Chemical and Materials Engineering
- Teacher: Ravi Sankannavar
Nanomaterials: an overview, zero, one and two-dimensional nanomaterials. Synthesis of nanomaterials: top-down and bottom-up approaches. Characterization of nanomaterials: characterization of nanomaterials using UV-Visible absorption spectroscopy (UV-Vis), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), raman spectroscopy (Raman), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR), atomic force microscopy (AFM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta potential, BET surface area analysis, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Properties of nanomaterials: mechanical, optical, electrical, and magnetic properties of nanomaterials. Application of nanomaterials: case studies on various applications such as energy storage devices, sensing, cancer therapy and anti-bacterial activity. Problems and challenges associated withnanomaterials.
Skip site announcements


